Перетяжка мебели — это популярный способ обновить и персонализировать интерьер, продлевая при этом жизнь
Промышленные светодиодные светильники являются революционным решением в сфере освещения производственных, складских и других коммерческих
Среди наиболее важных аксессуаров можно выделить чехлы и подставки для ножниц, средства для ухода
Дипломная работа – это кульминация академического пути студента, финальный этап образовательного процесса в вузе.
Насосное оборудование играет фундаментальную роль в современной индустрии, обеспечивая эффективное и надежное перемещение жидкостей
Выбор верхней одежды для зимы - это важный и в то же время захватывающий
Правильно подобранное пространство способствует созданию эффективной обучающей среды и способствует более глубокому погружению в
Выбор аксессуаров для автомобиля – это возможность выразить свою индивидуальность и придать транспортному средству
Ремонт диванов может включать в себя различные виды работ, в зависимости от характера повреждений
В жизни каждой дочери бывают моменты, когда она ощущает несравненную радость, тепло и поддержку,
Одним из наиболее востребованных и практичных решений для оптимизации жилого пространства является совмещение кухни
Поддержание чистоты и порядка в квартире является важным аспектом нашей повседневной жизни. Чистая и
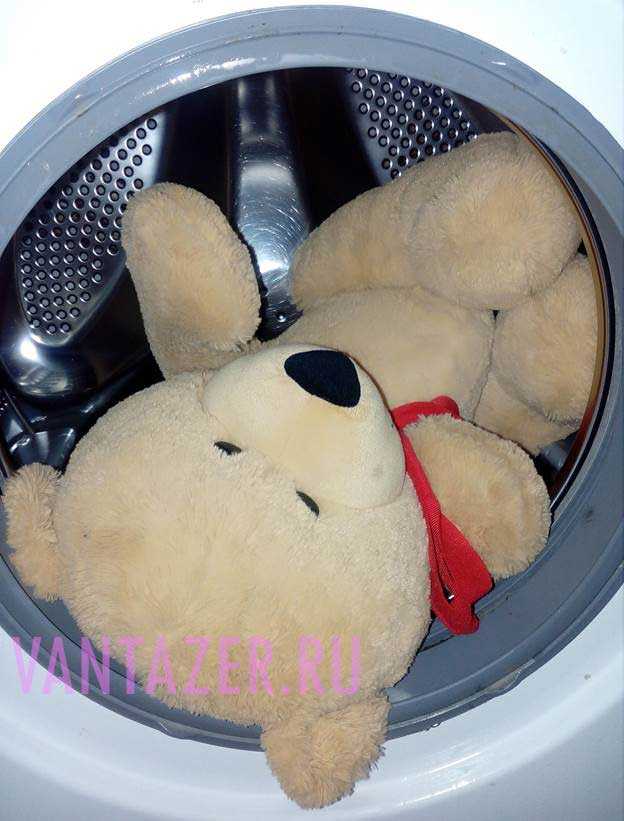
Узнайте как можно постирать мягкую музыкальную игрушку или плюшевого медведя в стиральной машине -
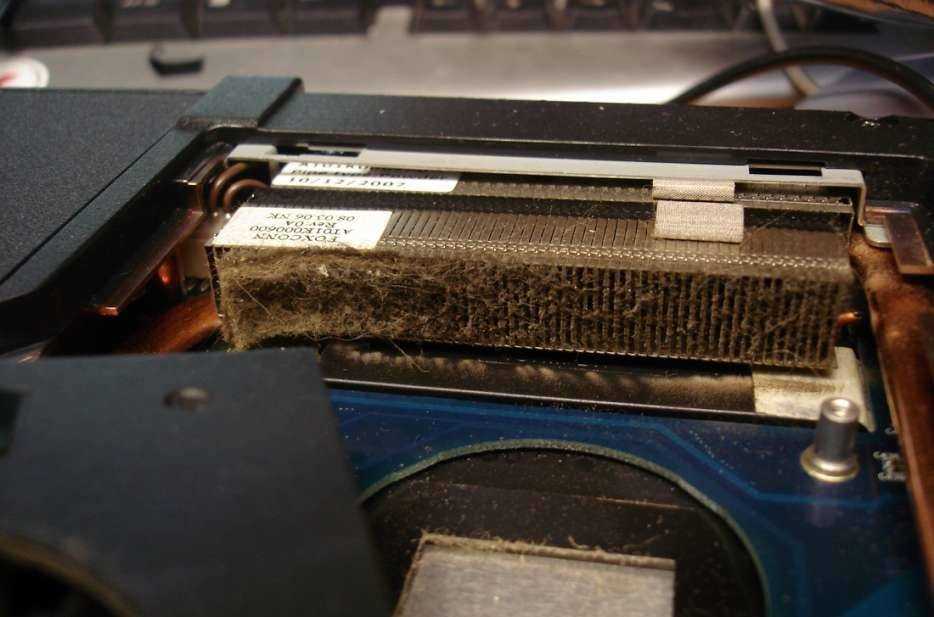
Как почистить ноутбук от пыли самостоятельно: это может каждый Ноутбук, как и персональный компьютер,
Курс доллара Центрального банка - это один из важнейших показателей, определяющих финансовое состояние и
В современном мире коммерческих и офисных помещений, куда каждый день приходит большое количество людей,
Прачечная – одна из важных подструктур сферы обслуживания. Современные прачечные обеспечивают стирку и последующую
Гостиная является центром дома, местом, где семья и друзья собираются для отдыха, развлечений и
Поломки холодильников могут быть различными: от неисправности компрессора, до замены уплотнительной резины или регулировки
Производство мебели в компании "Дизайн Мебель" является комплексным процессом, включающим несколько этапов.
Помолвочные кольца — это кольца, которые обычно обмениваются парой в знак предложения руки и
Уборка кухни – это задача, которая может стать настоящим испытанием даже для самых аккуратных
Каждый год дизайнеры и производители мягкой мебели представляют новые коллекции, которые отражают текущие тенденции и
Кварцевый ламинат - это современное покрытие для пола, которое сочетает в себе преимущества камня
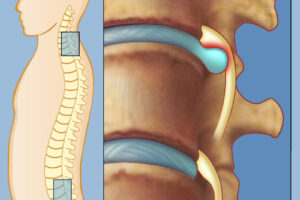
Протрузия позвоночника - это состояние, при котором диски между позвонками частично выступают за их